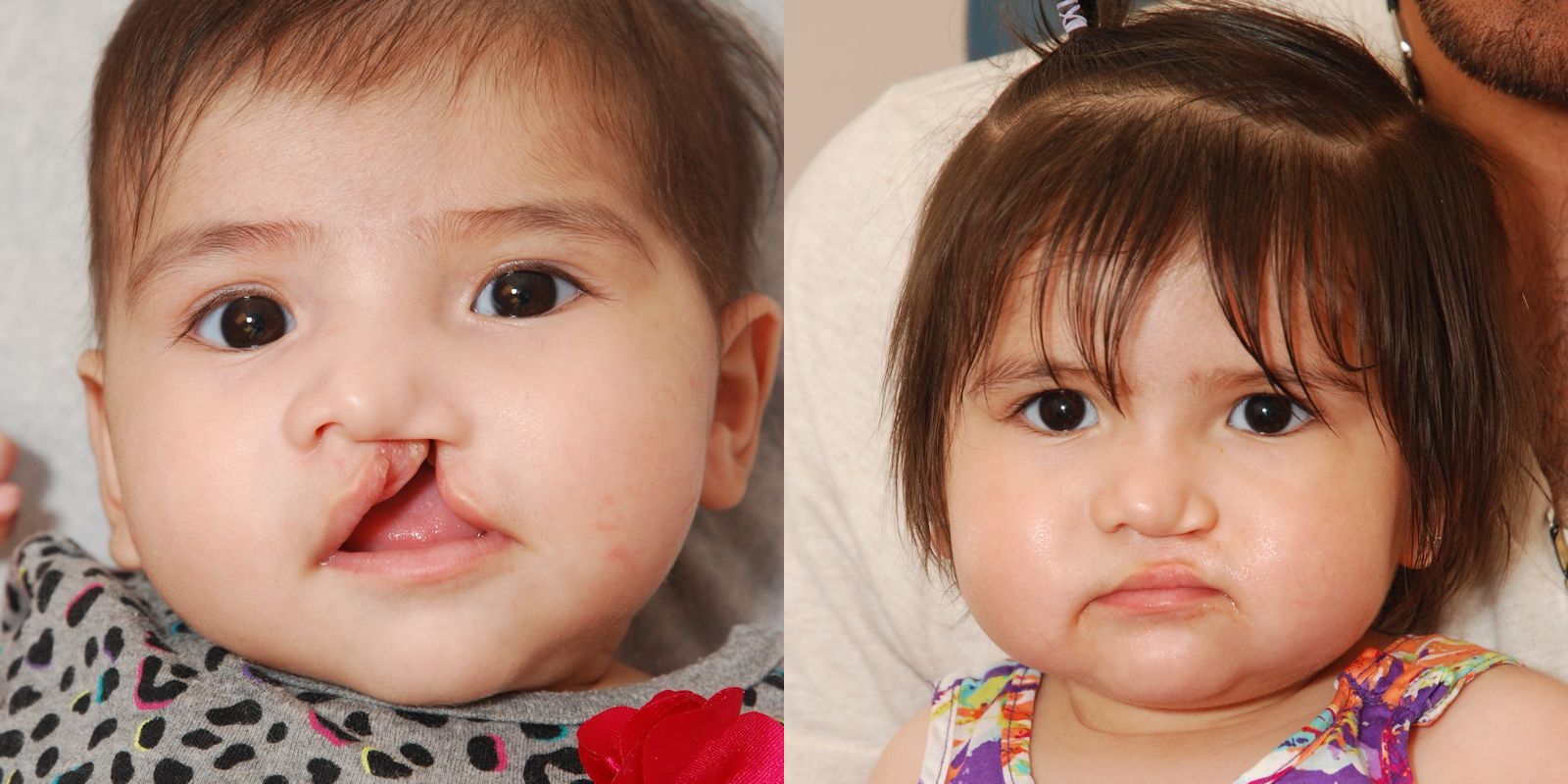
Cleft lip and cleft palate are openings or splits in the upper lip, the roof of the mouth (palate) or both. Cleft lip and cleft palate result when facial structures that are developing in an unborn baby don’t close completely.
Cleft lip and cleft palate are among the most common birth defects. They most commonly occur as isolated birth defects but are also associated with many inherited genetic conditions or syndromes.
Having a baby born with a cleft can be upsetting, but cleft lip and cleft palate can be corrected. In most babies, a series of surgeries can restore normal function and achieve a more normal appearance with minimal scarring.
Causes
Cleft lip and cleft palate occur when tissues in the baby’s face and mouth don’t fuse properly. Normally, the tissues that make up the lip and palate fuse together in the second and third months of pregnancy. But in babies with cleft lip and cleft palate, the fusion never takes place or occurs only part way, leaving an opening (cleft).
Researchers believe that most cases of cleft lip and cleft palate are caused by an interaction of genetic and environmental factors. In many babies, a definite cause isn’t discovered.
The mother or the father can pass on genes that cause clefting, either alone or as part of a genetic syndrome that includes a cleft lip or cleft palate as one of its signs. In some cases, babies inherit a gene that makes them more likely to develop a cleft, and then an environmental trigger actually causes the cleft to occur.
Treatment
The goals of treatment for cleft lip and cleft palate are to improve the child’s ability to eat, speak and hear normally and to achieve a normal facial appearance.
Care for children with cleft lip and cleft palate often involves a team of doctors and experts
Surgery
Surgery to correct cleft lip and palate is based on your child’s particular situation. Following the initial cleft repair, your doctor may recommend follow-up surgeries to improve speech or improve the appearance of the lip and nose.
Surgeries typically are performed in this order:
- Cleft lip repair — within the first 3 to 6 months of age
- Cleft palate repair — by the age of 12 months, or earlier if possible
- Follow-up surgeries — between age 2 and late teen years
Cleft lip and palate surgery takes place in a hospital. Your child will receive a general anesthetic, so he or she won’t feel pain or be awake during surgery. Several different surgical techniques and procedures are used to repair cleft lip and palate, reconstruct the affected areas, and prevent or treat related complications.
In general, procedures may include:
- Cleft lip repair. To close the separation in the lip, the surgeon makes incisions on both sides of the cleft and creates flaps of tissue. The flaps are then stitched together, including the lip muscles. The repair should create a more normal lip appearance, structure and function. Initial nasal repair, if needed, is usually done at the same time.
- Cleft palate repair. Various procedures may be used to close the separation and rebuild the roof of the mouth (hard and soft palate), depending on your child’s situation. The surgeon makes incisions on both sides of the cleft and repositions the tissue and muscles. The repair is then stitched closed.
- Ear tube surgery. For children with cleft palate, ear tubes may be placed to reduce the risk of chronic ear fluid, which can lead to hearing loss. Ear tube surgery involves placing tiny bobbin-shaped tubes in the eardrum to create an opening to prevent fluid buildup.
- Surgery to reconstruct appearance. Additional surgeries may be needed to improve the appearance of the mouth, lip and nose.
Surgery can significantly improve your child’s appearance, quality of life, and ability to eat, breathe and talk. Possible risks of surgery include bleeding, infection, poor healing, widening or elevation of scars, and temporary or permanent damage to nerves, blood vessels or other structures.